Describe 3 Market Problems That Prevent Efficient Allocation of Resources
The theory is that when consumers demand for goods exceeds supply prices go up which motivates both conservation of that good by consumers and increased production by businesses. Answer 1 of 3.
6 3 Market Failure Principles Of Economics
Planning failure might lead to resources wasted and consumers want not fulfilled.

. 1 increased demand temporary shortage -- raised price then production. Resources are allocated according to the needs of consumers. New higher Pe signals product scarcity 2 increased supply temporary surplus -- reduced production and prices.
This production method may not be the cheapest as profits play no part in the allocation of resources. But recently an increase in factors causing uncertainty from trade wars to Brexit and the global slowdown have exacerbated political infighting driving resource allocation challenges to new heights the Gartner report said. Price and Quantity Regulations.
There are two reasons theoretical and empirical. The higher profits are both the motive to produc. Optimum where MSB MSC.
Resources are allocated by consumer preferences. Market failures can be corrected through government intervention such as new laws or taxes. The resource more available and costs less.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. If a price regu. Attempting to bring about point C through force of regulation however runs into a.
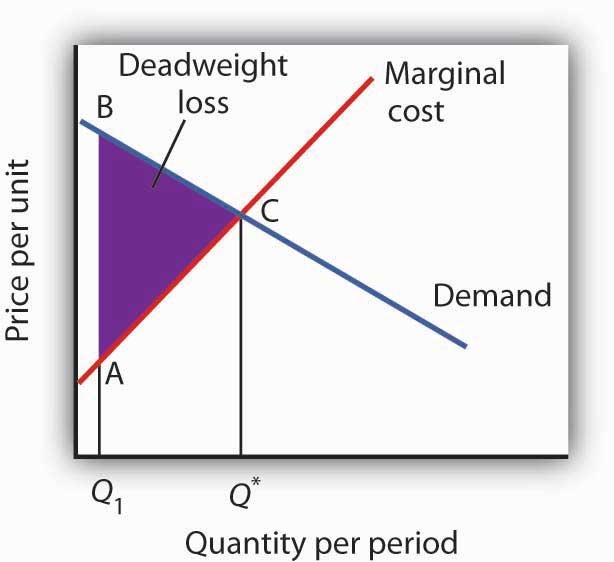
However if the firm did not pay for the external cost caused MSC would be greater than price and over-production over-consumption and a misallocation of societys scarce resources would occur. So market failure happens when the competitive outcome of markets is not efficient from the point of view of society as a whole. Here are the three main ones.
Lower Pe signals less scarcity of a resource and more people use it opportunity cost. Allocative efficiency is when resources are allocated to their most valued use as in the best use for society as a whole - Social Optimum. Political infighting and bureaucracy have long been obstacles.
Signals Think of prices as a traffic light. Price regulations include price ceilings which sets the highest legal price and price floors which set the lowest legal price. Answer 1 of 3.
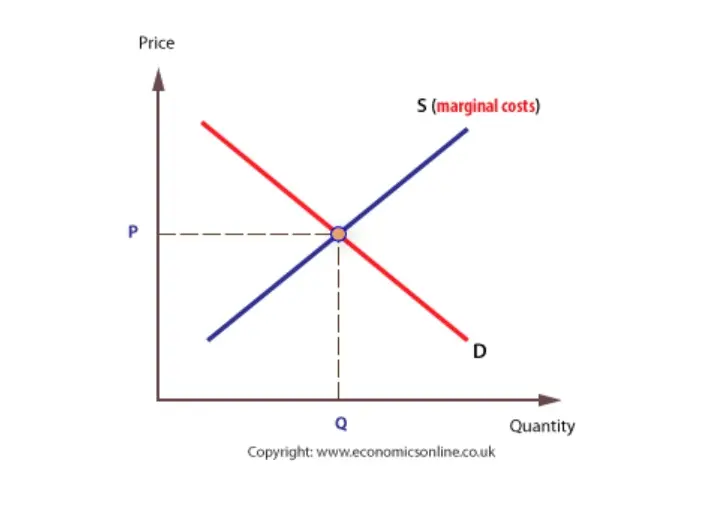
Price regulations include price ceilings which sets the highest legal price and price floorswhich set the lowest legal price. Allocative efficiency automatically occurs where price equals marginal cost PMC. Who are the experts.
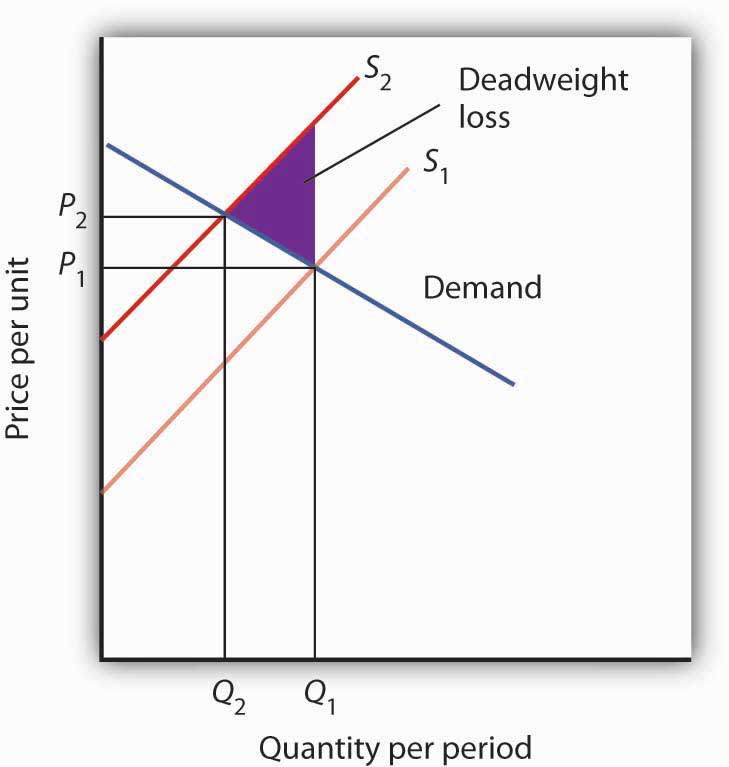
There are many instances where the free market fails to achieve an efficient allocation. Market failure will lead to productive and allocative inefficiencies. Consumers reduce demand at the new price.
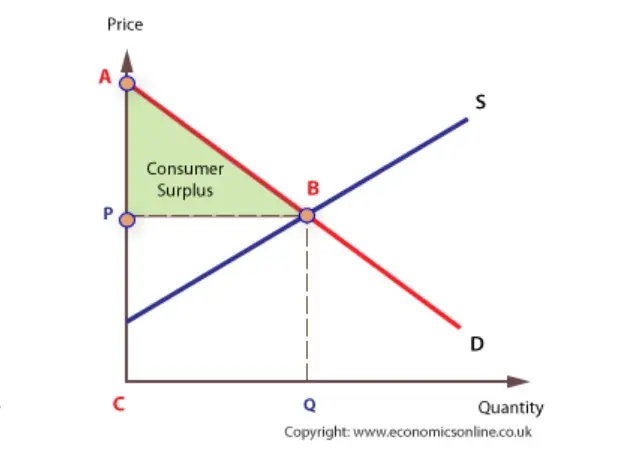
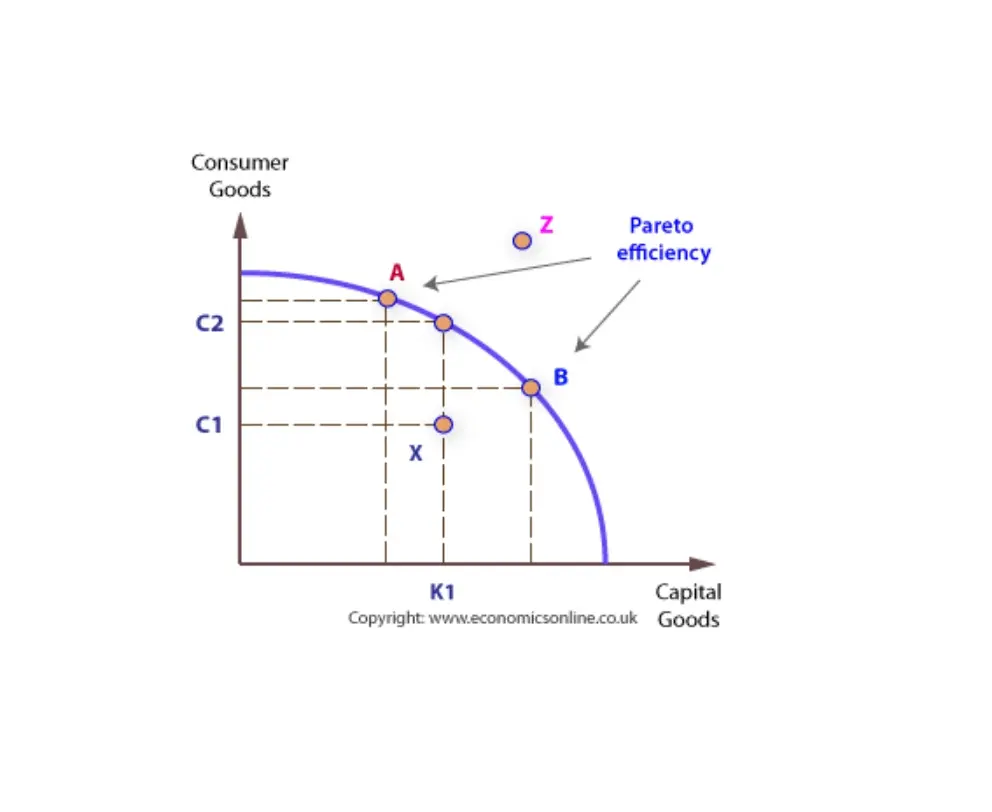
What three problems in the free market work against the efficient allocation of resources. Pareto efficiency Consumer and producer surplus Deadweight loss Definitions of Efficiency Engineering efficiency output per unit of input example. Allocative efficiency - resources are allocated according to their highest.
If a price regulation makes the equilibrium price illegal it leads to inefficiency. Market failure can be caused by a lack of information market control public goods and externalities. 1Imperfect conpetition 2spillover costsexternalities3Imperfect Information.
When consumers want and demand more. Either condition will mean that decision makers are not faced with the marginal benefits and costs of their choices. Describe the meaning of externalities as the failure of the market to achieve a social.
Mixed economy is one that combines the characteristics of both command and free market economy. The profit motive also encourages producers to be more innovative and resource allocation is directed towards better products and services. What three problems in the free market work against the efficient allocation of resources.
Market failure occurs when a free market fails to deliver an efficient allocation of resources. Using markets for allocation of resources is generally efficient better and cheaper. We review their content and use your feedback to.
It can provide quicker means of business transactions between buyers and sellers. The key obstacles to achieving an efficient allocation of resources in a market are. Prices can encourage or discourage production.
Transactions then the market has achieved an efficient allocation of resources This means that all of the resources that both buyers and sellers have are allocated so that these buyers and sellers are as well off as possible. The free market has the only mechanism by which to determine what efficient allocation of resources even means. Efficient allocation of resources concerns using resources as productively and efficiently as possible.
For these reasons private market transactions between buyers and sellers are usually. A relatively high price is. A market tends to create and maintain somewhat a balance between demand and supply so that there is no surplus and shortage of products.
The key obstacles to achieving an efficient allocation of resources in a market are. What are the obstacles to achieving an efficient allocation of resources in the market economy. Miles per gallon Production efficiency cannot produce more of one good without producing less of another good using more inputs points on the PPF Definitions of Efficiency.
Price and Quantity Regulations. It concerns resources possessing the three types of efficiency. Technical efficiency - resources can be used to achieve a greater output from the same level of inputs.
This problem has been solved. Conversely if the production of a good conferred net positive externalities on society then there would be under-production and under-consumption at the free market price and again a. Prices as an Incentive Prices communicate to both buyers and sellers whether goods or services are scarce or easily available.
In fact efficient allocation of resources would occur at point C since the value to the consumers of the last unit bought and sold in this market is equal to the marginal cost of producing it. Markets will not generate an efficient allocation of resources if they are not competitive or if property rights are not well defined and fully transferable. The profit motive forces producers to reduce costs and use the resources more efficiently avoids wastage.
Imperfect competition spillover costs imperfect information- not.

Ap Macroeconomics Review Every Graph You Need To Know For The Exam Youtube Macroeconomics Teaching Economics Learn Economics

Important Formula And Example For Ie Industrial Engineering Engineering Formula
6 3 Market Failure Principles Of Economics

Free Market Intelligent Economist
Methods In Microeconomic And Macroeconomic Issues Springerlink
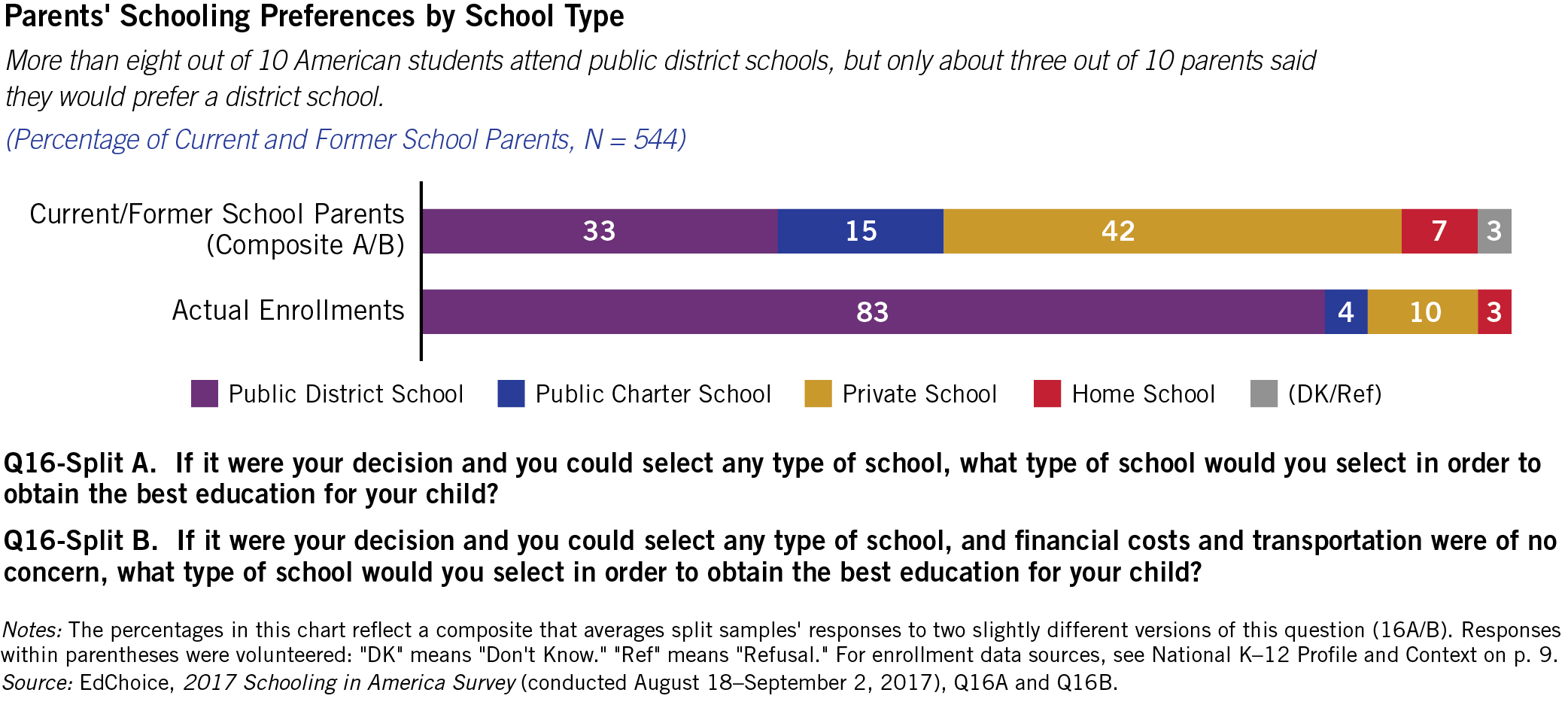
Defining Market Failure With Examples Edchoice
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Price_Elasticity_Affect_Supply_Feb_2020-02-9e07b9c680ac4926adba76eded63d372.jpg)
How Does Price Elasticity Affect Supply
4 P S Of Marketing Overview Marketing Mix Extensions
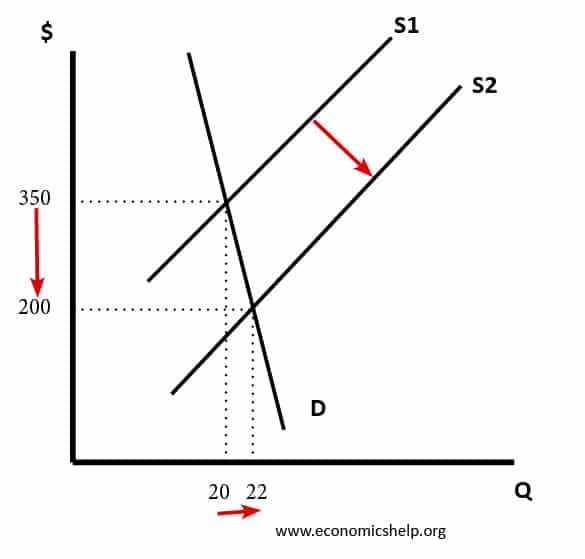
Problems Of Agriculture Market Failure Economics Help
/laissez-faire-definition-4159781-V2-828107953ee443f1bdeaaaba9b35759b.jpg)
What Is Laissez Faire Economic Theory

Market Failure Definition Causes And How To Address
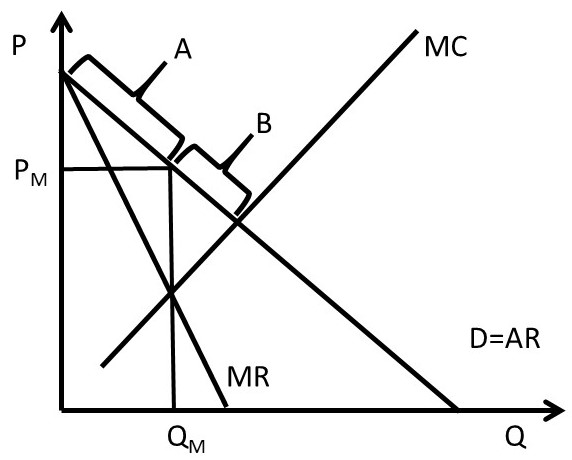
Chapter 4 Pricing With Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets

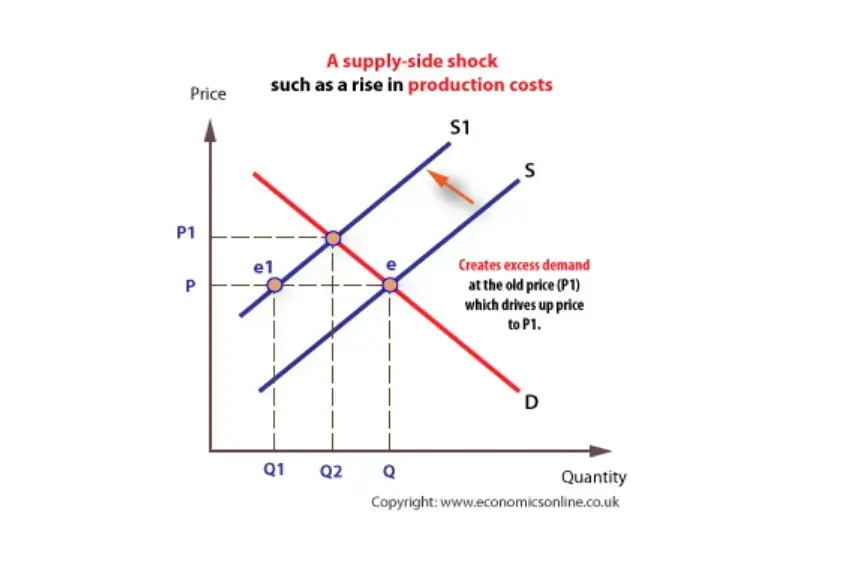

Comments
Post a Comment